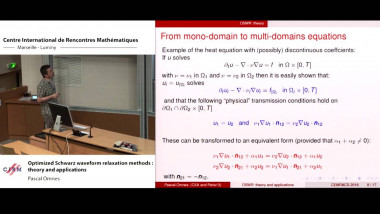
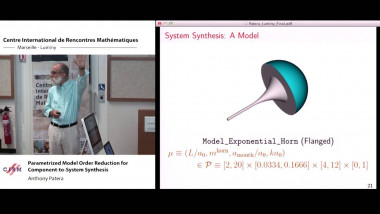
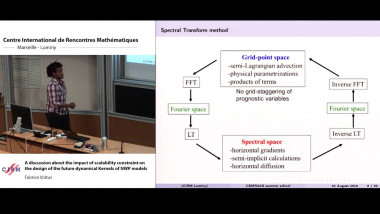
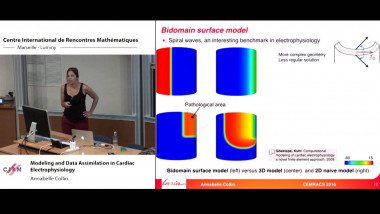
High-order Magnus integrators for non-autonomous linear evolution equations
Also appears in collection : New challenges in mathematical modelling and numerical simulation of superfluids / Nouveaux défis dans la modélisation mathématique et la simulation numérique de systèmes superfluides
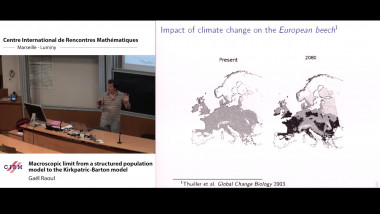
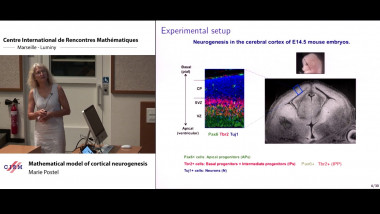
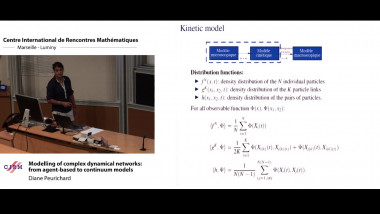
The class of commutator-free Magnus integrators is known to provide a favourable alternative to standard interpolatory Magnus integrators, in particular for large-scale applications arising in the time integration of non-autonomous linear evolution equations. A high-order commutator-free Magnus integrator is given by a composition of several exponentials that comprise certain linear combinations of the values of the defining operator at specified nodes. Due to the fact that previously proposed commutator-free Magnus integrators of order five or higher involve negative coefficients in the linear combinations, severe instabilities are observed for spatially semi-discretised partial differential equations of parabolic type or for master equations describing dissipative quantum systems, respectively. In order to remedy this issue, two different approaches for the design of efficient Magnus integrators of orders four, five, and six are pursued: (i) the study of commutator-free Magnus integrators involving complex coefficients with positive real part, and (ii) the study of unconventional Magnus integrators that comprise in addition a single exponential involving a commutator. Numerical experiments for test equations of Schrödinger and parabolic type confirm that the identified novel Magnus integrators are superior to Magnus integrators previously proposed in the literature.



























































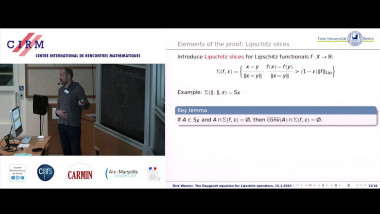



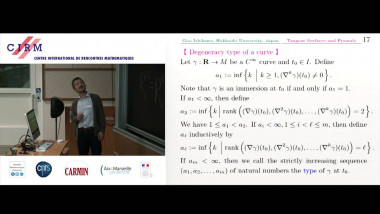






































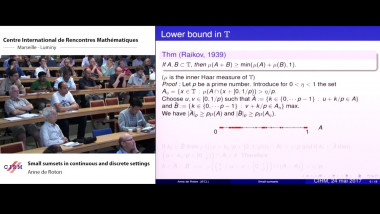
![$k$-sum free sets in $[0,1]$](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/2015-09-10_de_Roton-video--19cf70874d3c5af7378c268cab865b06.jpg)