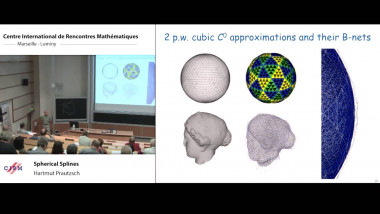
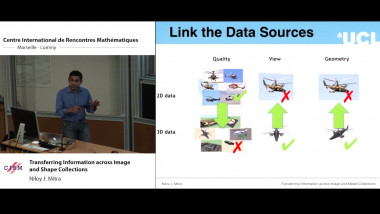
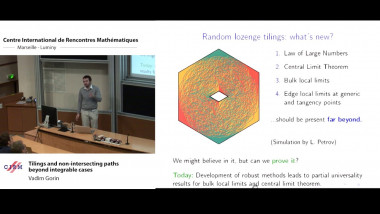
Nonlinear analysis with resurgent functions
De David Sauzin
Apparaît également dans la collection : Real analytic geometry and trajectories of vector fields / Géométrie analytique réelle et trajectoires de champs de vecteurs
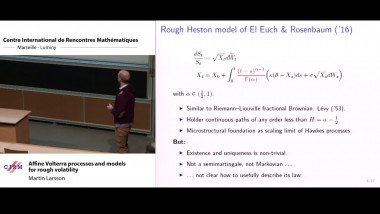
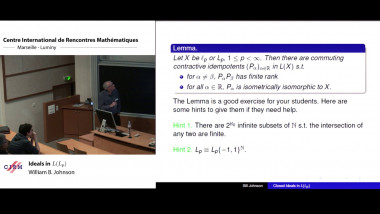
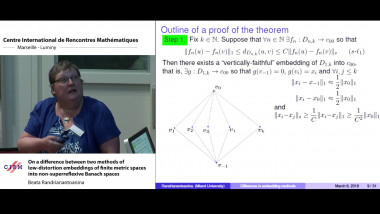
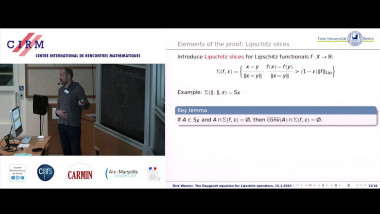
Ecalle’s resurgent functions appear naturally as Borel transforms of divergent series like Stirling series, formal solutions of differential equations like Euler series, or formal series associated with many other problems in Analysis and dynamical systems. Resurgence means a certain property of analytic continuation in the Borel plane, whose stability under con- volution (the Borel counterpart of multiplication of formal series) is not obvious. Following the analytic continuation of the convolution of several resurgent functions is indeed a delicate question, but this must be done in an explicit quan- titative way so as to make possible nonlinear resurgent calculus (e.g. to check that resurgent functions are stable under composition or under substitution into a convergent series). This can be done by representing the analytic continuation of the convolution product as the integral of a holomorphic n-form on a singular n-simplex obtained as a suitable explicit deformation of the standard n-simplex. The theory of currents is convenient to deal with such integrals of holomorphic forms, because it allows to content oneself with little regularity: the deformations we use are only Lipschitz continuous, because they are built from the flow of non-autonomous Lipschitz vector fields.


































































































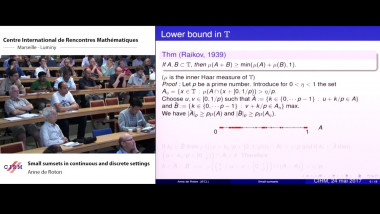
![$k$-sum free sets in $[0,1]$](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/2015-09-10_de_Roton-video--19cf70874d3c5af7378c268cab865b06.jpg)