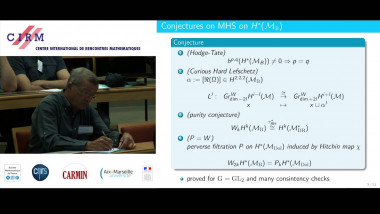
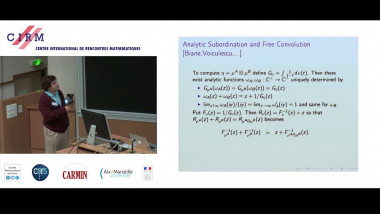
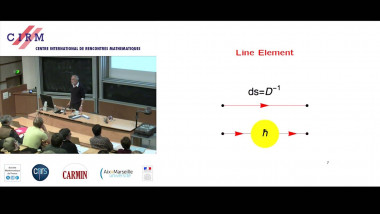
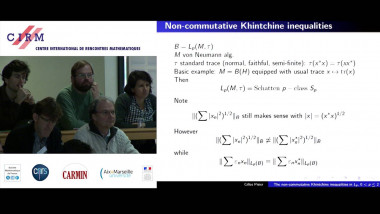
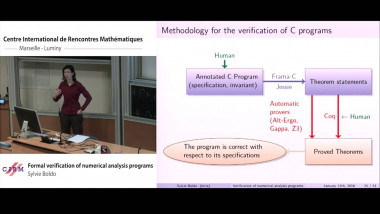
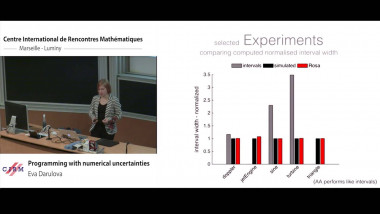
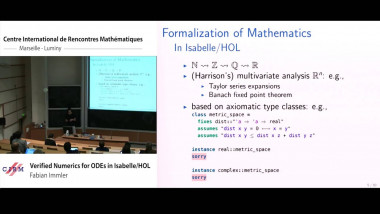
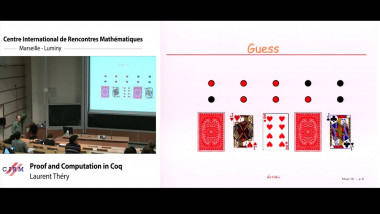
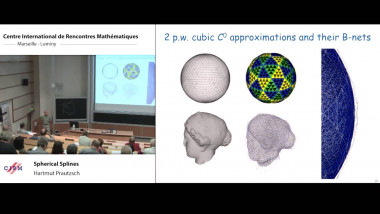
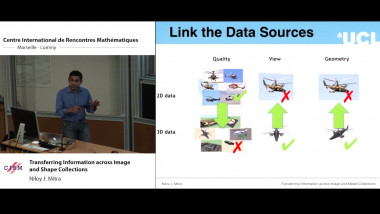
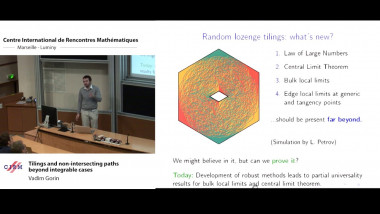
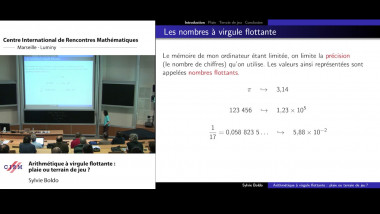
Independence of normal words
Apparaît également dans la collection : Computability, randomness and applications / Calculabilité, hasard et leurs applications
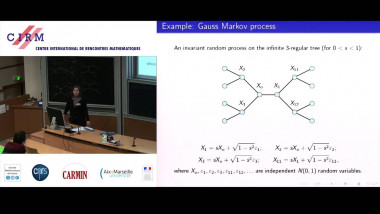
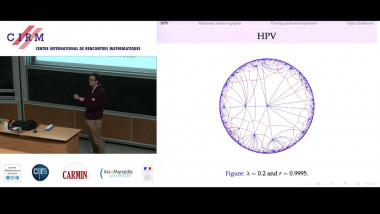
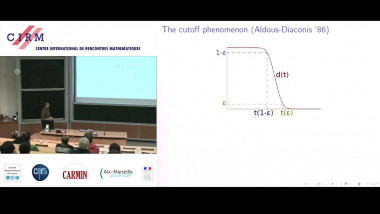
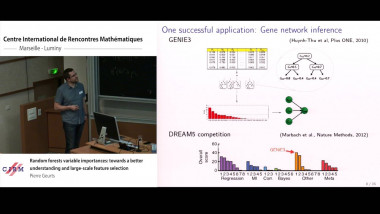
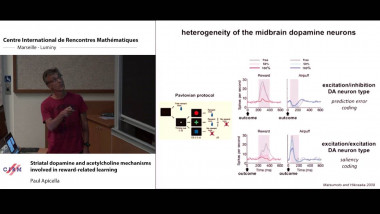
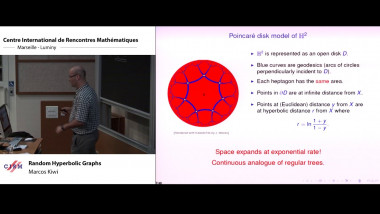
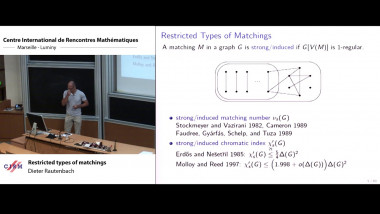
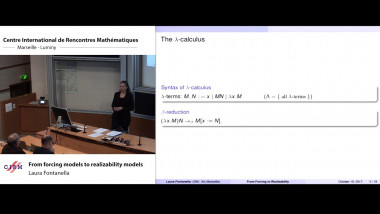
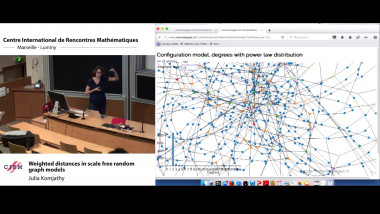
Recall that normality is a elementary form of randomness: an infinite word is normal to a given alphabet if all blocks of symbols of the same length occur in the word with the same asymptotic frequency. We consider a notion of independence on pairs of infinite words formalising that two words are independent if no one helps to compress the other using one-to-one finite transducers with two inputs. As expected, the set of independent pairs has Lebesgue measure 1. We prove that not only the join of two normal words is normal, but, more generally, the shuffling with a finite transducer of two normal independent words is also a normal word. The converse of this theorem fails: we construct a normal word as the join of two normal words that are not independent. We construct a word x such that the symbol at position n is equal to the symbol at position 2n. Thus, x is the join of x itself and the subsequence of odd positions of x. We also show that selection by finite automata acting on pairs of independent words preserves normality. This is a counterpart version of Agafonov's theorem for finite automata with two input tapes. This is joint work with Olivier Carton (Universitéé Paris Diderot) and Pablo Ariel Heiber (Universidad de Buenos Aires).



































































































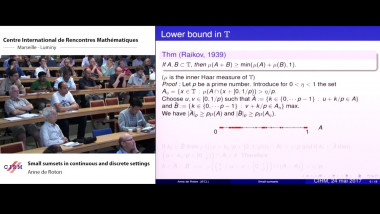
![$k$-sum free sets in $[0,1]$](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/2015-09-10_de_Roton-video--19cf70874d3c5af7378c268cab865b06.jpg)