Large-scale machine learning and convex optimization 2/2
De Francis Bach
Apparaît également dans la collection : Thematic month on statistics - Week 1: Statistical learning / Mois thématique sur les statistiques - Semaine 1 : apprentissage
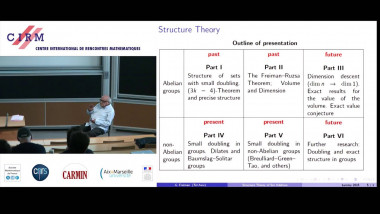
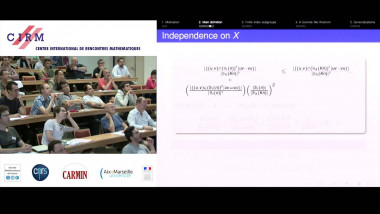
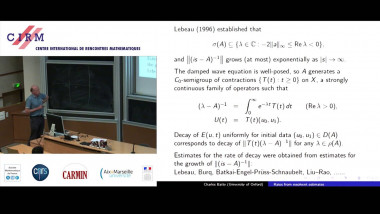
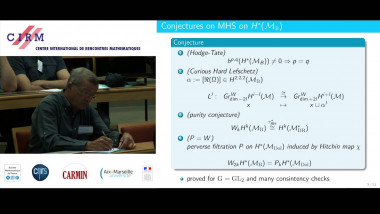
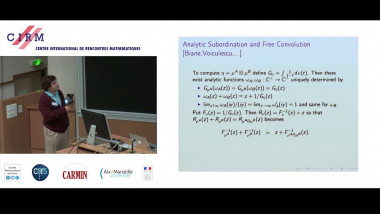
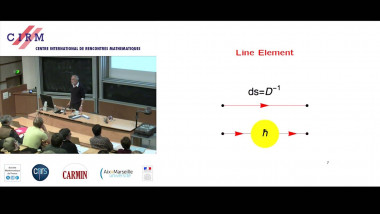
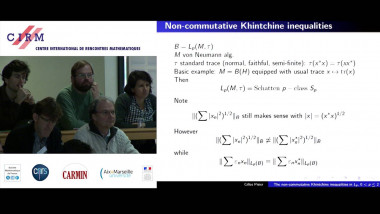
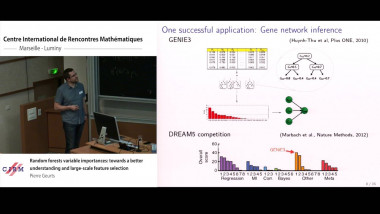
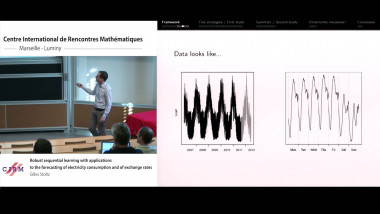
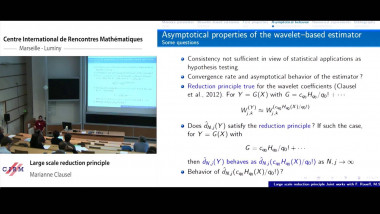
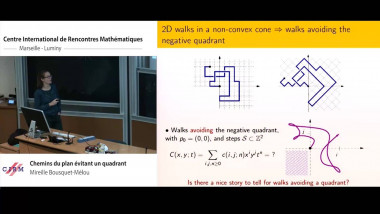
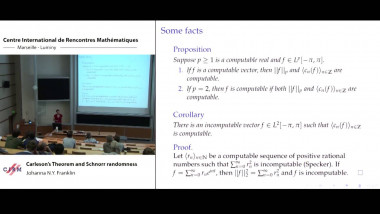
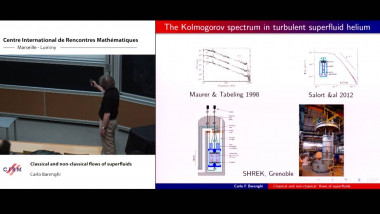
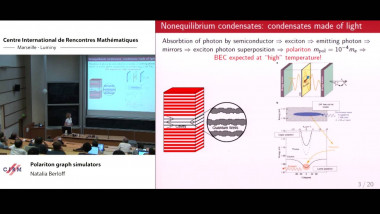
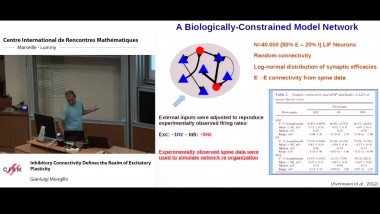
Many machine learning and signal processing problems are traditionally cast as convex optimization problems. A common difficulty in solving these problems is the size of the data, where there are many observations ("large n") and each of these is large ("large p"). In this setting, online algorithms such as stochastic gradient descent which pass over the data only once, are usually preferred over batch algorithms, which require multiple passes over the data. Given n observations/iterations, the optimal convergence rates of these algorithms are $O(1/\sqrt{n})$ for general convex functions and reaches $O(1/n)$ for strongly-convex functions. In this tutorial, I will first present the classical results in stochastic approximation and relate them to classical optimization and statistics results. I will then show how the smoothness of loss functions may be used to design novel algorithms with improved behavior, both in theory and practice: in the ideal infinite-data setting, an efficient novel Newton-based stochastic approximation algorithm leads to a convergence rate of $O(1/n)$ without strong convexity assumptions, while in the practical finite-data setting, an appropriate combination of batch and online algorithms leads to unexpected behaviors, such as a linear convergence rate for strongly convex problems, with an iteration cost similar to stochastic gradient descent.


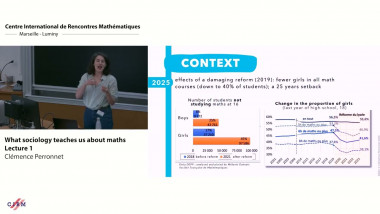










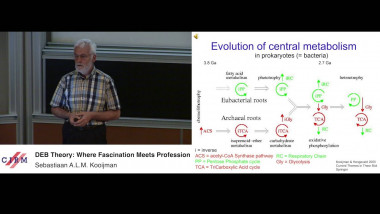






















































































![$k$-sum free sets in $[0,1]$](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/2015-09-10_de_Roton-video--19cf70874d3c5af7378c268cab865b06.jpg)