Arborescent Koszul-Tate resolutions and BFV for singular coisotropic reductions
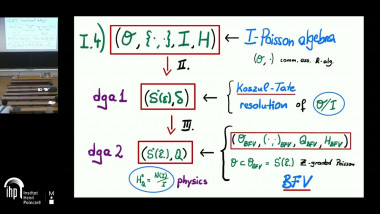
Let I be an ideal in a commutative (associative) algebra O. Starting from a resolution of O/I as an O-module, we construct a Koszul-Tate resolution for this quotient, i.e.\ a graded symmetric algebra over O with a differential which provides simultaneously a resolution as an O-module. This algebra resolution has the beautiful structure of a forest of decorated trees and is related to an A-infinity algebra on the original module resolution. Considering O to be a Poisson algebra and I a finitely generated Poisson subalgebra, we use the above construction to obtain the corresponding BFV formulation. Its cohomology at degree zero is proven to coincide with the reduced Poisson algebra N(I)/I, where N(I) is the normaliser of I inside O, thus generalising ordinary coisotropic reduction to the singular setting. As an illustration we use the example where O consists of functions on T^*(\R^3) and I is the ideal generated by angular momenta.
This is joint work with Aliaksandr Hancharuk and, in part, with Camille Laurent-Gengoux.