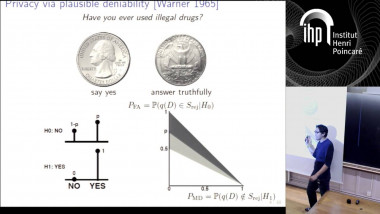
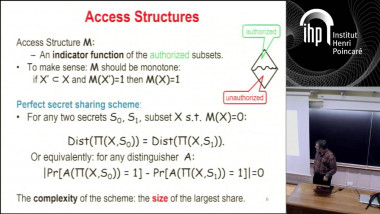
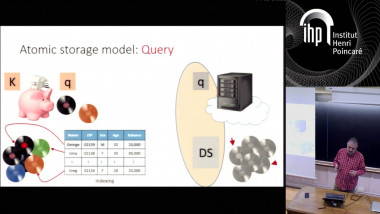
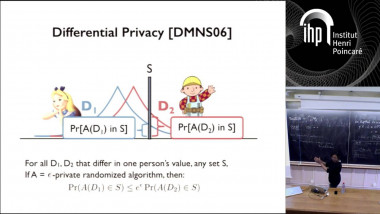
Quantum lower bound for inverting a permutation with advice
Hellman proved that any permutation can be inverted non-trivially fast given pre-computed information. Any permutation $f:[N]−>[N]$ can be inverted in time $T$ given a pre-computed data structure of size $N/T$, up to lower-order terms. In the black-box model, Yao proved the optimality of this trade-off. In particular, a data structure of size of the order o $\sqrt{N}$ allows inversion time of the order o $\sqrt{N}$. Using Grover's algorithm, a quantum algorithm is able to invert any permutation $f:[N]−>[N]$ in time order of $\sqrt{N}$. What gain is possible given pre-computed data? Could we hope for time and data size to be both of the order of $N^{1/4}$? In the black-box model, we show that, given data of size $S$, the time as to be at least of the order of $\sqrt{N/S}$, and so either time or size have to be at least $N^{1/3}$. Our lower bound is not known to be tight, and probably it is not: we believe that, in the black-box model, there is no quantum algorithm that achieves time less than $\sqrt{N}$ using data size less than $\sqrt{N}$. (Joint work with Nayebi, Aaronson and Belov)