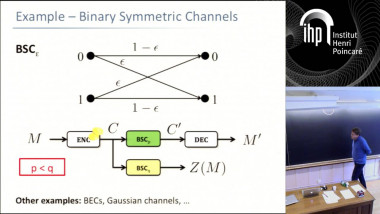
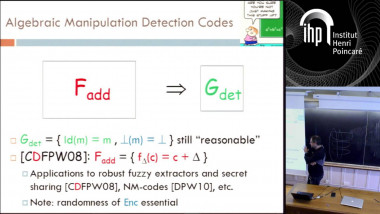
How to Share a Secret, Infinitely
By Moni Naor
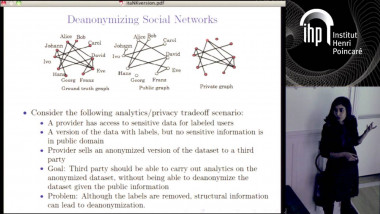
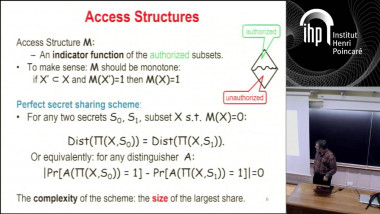
Secret sharing schemes allow a dealer to distribute a secret piece of information among several parties such that only qualified subsets of parties can reconstruct the secret. The collection of qualified subsets is called an access structure. The best known example is the k-threshold access structure, where the qualified subsets are those of size at least k. When k=2 and there are n parties, there are schemes where the size of the share each party gets is roughly logn bits, and this is tight even for secrets of 1bit. In these schemes, the number of parties n must be given in advance to the dealer. We consider the case where the set of parties is not known in advanced and could potentially be infinite. Our goal is to give the party arriving at step ta small share as possible as a function of t. Our main result is such a scheme for the k-threshold access structure where the share size of party t is (k−1)logt plus o(logt)poly(k). For k=2 we observe an equivalence to prefix codes and present matching upper and lower bounds of the form logt+loglogt+logloglogt+⋯+O(1). Finally, we show that for any access structure there exists such a secret sharing scheme with shares of size 2t−1. Joint work with Ilan Komargoski and Eylon Yogev