Stochastic modeling for population dynamics: simulation and inference - Part 2
Apparaît également dans la collection : Thematic Month Week 1: PDE and Probability for Biology / Mois thématique Semaine 1 : EDP et probabilité pour la biologie
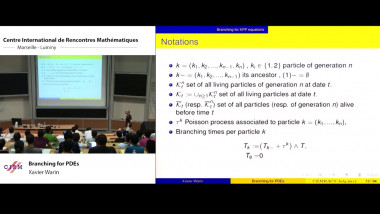
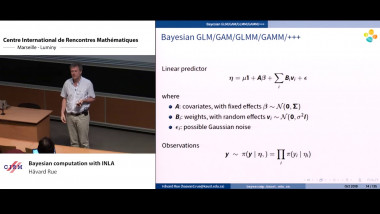
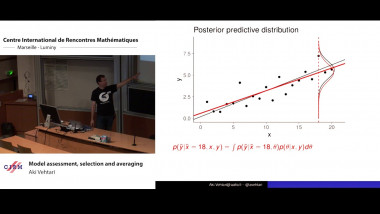
The aim of this course is to present some examples of stochastic models suitable for population dynamics. The first part will introduce a class of continuous time models called piecewise deterministic Markov processes (PDMPs). Their trajectories are deterministic with jumps at random times. They are especially suitable to model phenomena with different time scales: a fast time-sacla corresponding to the deterministic behaviour and a slow time-scale corresponding to the jumps. I'll present different biological systems that can be modelled by PDMPs, explain how they can be simulated. The second part will focus on random models for cell division when the whole branching population is taken into account. I'll present two data sets from biological experiments trying to determine whether cell division is symmetric or not. I'll explain how statistic tools can help answer this question.