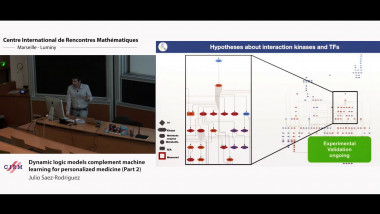
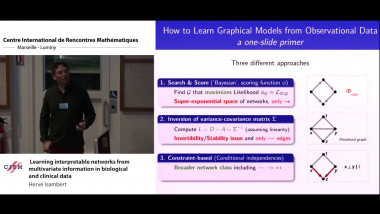
Learning interpretable networks from multivariate information in biological and clinical data
The reconstruction of graphical models (or networks) has become ubiquitous to analyze the rapidly expanding, information-rich data of biological or clinical interest. I will outline some network reconstruction methods and applications to large scale datasets. In particular, our group has developped information-theoretic methods and machine learning tools to infer and analyze interpretable graphical models from large scale genomics data (single cell transcriptomics, tumor expression and mutation data) as well as clinical data (analysis of medical records from breast cancer patients, Institut Curie, and from elderly patients with cognitive disorders, La Pitie-Salpetriere).