Signal processing tutorial - part 2
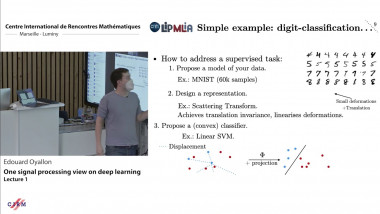
Processing signals presents many challenges by the quantity, structure, faults, heterogeneity of sensor data recorded over time. Supporting decisions using prediction or detection based on data streams naturally calls Machine Learning techniques (and theory!) for backup. The latter field has witnessed a tremendous development since the publication of Vladimir Vapnik’s best-seller ’The Nature of Statistical Learning’ and the invention of Support Vector Machines, Bagging, Boosting and Random Forests between 1995 and 1999 until the latest technological breakthroughs based on Deep Learning. However, most of its reference frameworks and methods consider vector observations which are essentially invariant up to a permutation of the indices of vector components. Beyond the obvious approach of featurization (or embedding) time series into vectors of characteristics (features), there are other more subtle interactions between the two fields of SP and ML but they first need to address some fundamental questions such as: - how to monitor the lack of stationarity in time - dependent data - how to supervise such data - what is the objective of learning (prediction goal) in this context, and more generally what can be learned with signals - how to account for additional structure in signals - how Signal Processing as a field may benefit from modern optimization techniques
The purpose of this course is to offer an overview on some Signal Processing problems from the angle of Machine Learning philosophy and techniques in order to develop insights on the fundamental questions formulated above. In other terms, this is not a standard course on Signal Processing and we may skip some of the very fundamental concepts that would belong to such a course.
The topics presented in this doctoral course will include: - local stationarity - event detection methodology - prediction problems with signals - representation learning - graph signal processing In the practical sessions, a concrete example in the context of precision medicine will be developed. In particular, the central issues of segmentation, quantification, representation will be addressed with code.