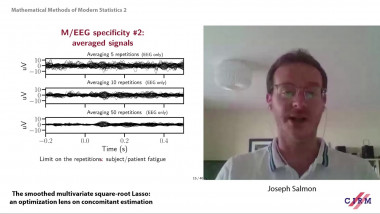
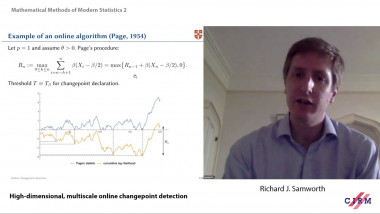
High-dimensional, multiscale online changepoint detection
We introduce a new method for high-dimensional, online changepoint detection in settings where a p-variate Gaussian data stream may undergo a change in mean. The procedure works by performing likelihood ratio tests against simple alternatives of different scales in each coordinate, and then aggregating test statistics across scales and coordinates. The algorithm is online in the sense that its worst-case computational complexity per new observation, namely O(p2log(ep)), is independent of the number of previous observations; in practice, it may even be significantly faster than this. We prove that the patience, or average run length under the null, of our procedure is at least at the desired nominal level, and provide guarantees on its response delay under the alternative that depend on the sparsity of the vector of mean change. Simulations confirm the practical effectiveness of our proposal.