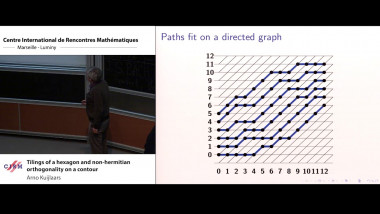
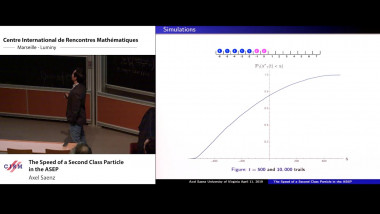
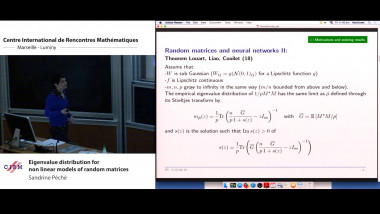
Eigenvalue distribution for non linear models of random matrices
The talk concerned with the asymptotic empirical eigenvalue distribution of a non linear random matrix ensemble. More precisely we consider $M= \frac{1}{m} YY^²$ with $Y=f(WX)$ where W and X are random rectangular matrices with i.i.d. centered entries. The function f is applied pointwise and can be seen as an activation function in (random) neural networks. We compute the asymptotic empirical distribution of this ensemble in the case where W and X have subGaussian tails and f is smooth. This extends a result of [PW17] where the case of Gaussian matrices W and X is considered. We also investigate the same questions in the multi-layer case, regarding neural network applications.