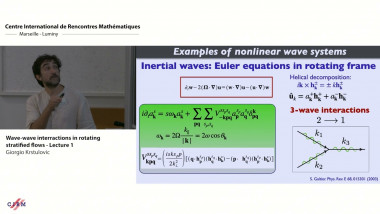
Wave-wave interactions in rotating stratified flows - lecture 1
Internal and inertial waves propagate in the bulk of rotating stratified fluids and play an important role in oceans and atmospheres. They interact nonlinearly, triggering instabilities and energy transfers along scales in a cascade process. In the first lecture, I will briefly introduce the general wave turbulence theory, including somehints on the derivation of the wave kinetic equation (WKE) in the general case. Then, I will discuss how we use the WKE to describe wave turbulent cascades and when this description is valid mathematically and then expected to be realisable in experiments and nature. In the second lecture, I will apply the concept of wave turbulence to the case of rotating andstratified fluids, explain the main theoretical difficulties and give an overview of some of the current experiments and simulations.





















![[1247] Dérivation de l'équation de Boltzmann en temps long à partir d'une dynamique de sphères dures](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/SeminaireBourbaki.png)




