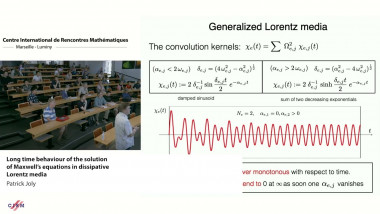
From Herglotz-Nevanlinna functions to completely monotonic functions
A Herglotz-Nevanlinna function is a holomorphic function $f$, defined in the upper half-plane $\mathbb{H}:=\{z \in \mathbb{C} \mid \Im z>0}$, such that $\Im f(z) \geq 0$ for all $z \in \mathbb{H}$, and they are the functions in focus at the present conference. These functions are also called Pick functions, and they are characterized as the functions of the form$$f(z)=\alpha z+\beta+\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{t z+1}{t-z} d \tau(t), \quad z \in \mathbb{H}$$where $\alpha \geq 0, \beta \in \mathbb{R}$ and $\tau$ is a positive finite measure on $\mathbb{R}$. Since $\mathbb{H}$ is a simply connected domain, caracterization of this class of functions is the same as characterization of the set of non-negative harmonic functions in $\mathbb{H}$ and by conformal mapping this set is in one-to-one correspondence with the set of non-negative harmonic functions in the unit disc. We shall discuss various subclasses of Pick functions and their relation to other important classes of functions such as the completely monotonic functions and the subclass of Stieltjes functions. We recall that these classes are the functions $f:] 0, \infty[\rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ of the form$$f(x)=\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-s x} d \mu(s), \quad \text { resp. } f(x)=a+\int_{0}^{\infty} \frac{d \mu(s)}{x+s}$$where $a \geq 0$ and $\mu$ is a non-negative measure on $[0, \infty[$.At the 7 th OPSFA, Copenhagen 2003 , we posed the problem of determining the largest value $\alpha=\alpha^{²}>0$ for which $f_{\alpha}(x)=e^{\alpha}-(1+1 / x)^{\alpha x}, x>0$ is a completely monotonic function, and it was noticed that $1 \leq \alpha^{²}<3$ and that graphs suggested that $\alpha^{²}>2$. The value has now been calculated with 20 decimals starting with $\alpha^{²} \approx 2.29965$.This is based on a recent result obtained in collaboration with Massa and Peron from Brazil. We have found a family $\varphi_{\alpha}, \alpha>0$ of entire functions such that$$f_{\alpha}(x)=\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-s x} \varphi_{\alpha}(s) d s, \quad x>0 .$$We showed that each function $\varphi_{\alpha}$ has an alternating power series expansion, whose coefficients are determined as an explicit sequence of polynomials in $\alpha$. It is therefore possible to calculate as accurately as desired for which values of $\alpha$ the function $\varphi_{\alpha}$ is non-negative on $\left[0, \infty\left[\right.\right.$. It turned out that the functions $\varphi_{\alpha}$ are 'close' to the well known Bessel function $J_{1}$ when $\alpha$ is large, and 'close' to the Lambert $W$ function, when $\alpha$ is small.