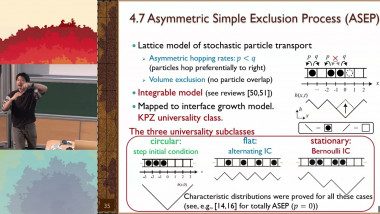
Introduction to the Physics of the KPZ Universality Class (3/3)
De Kazumasa Takeuchi

Nonequilibrium Point Processes with Long-range Correlations Generated by Stochastic Resetting (3/3)
De Satya N. Majumdar
Apparaît dans la collection : On Future Synergies for Stochastic and Learning Algorithms / Sur les synergies futures autour des algorithmes d'apprentissage et stochastiques
The two workhorses of molecular simulation are molecular dynamics and Markov-chain Monte Carlo. In this talk we compare them with an alternative: 'Event chain Monte Carlo' in which detailed balance is replaced by the weaker balance condition. We characterise the large scale dynamics of each method pointing out where event chains can give rise to more efficient or more accurate calculations. By optimising the splitting of interactions in event chain methods we show (in hard sphere systems) that we are able to further accelerate the sampling of density modes.
