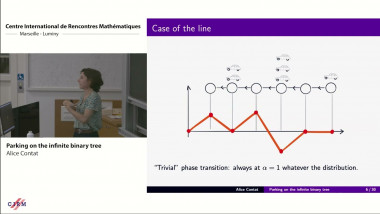
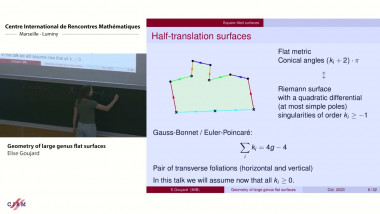
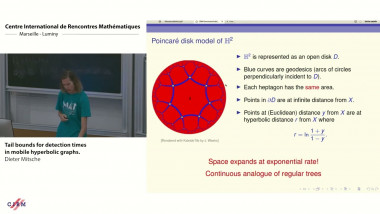
The geometry of random genus-0 hyperbolic surfaces via trees
De Timothy Budd
In this talk I will discuss a bijection between the moduli space of genus-0 hyperbolic surfaces with a distinguished cusp and certain labeled trees, analogous to known tree bijections in the combinatorics of planar maps. The Weil-Petersson measure on the moduli space takes a simple form at the level of the trees, and gives a bijective interpretation to the coefficients in the Weil-Petersson volume polynomials. The labels on the trees give precise information about geodesic distances in the surface, which can be used to study the geometry of random hyperbolic surfaces sampled from the Weil-Petersson measure. In particular, the random genus-0 hyperbolic surface with $n$ cusps is shown to converge as a metric space, after rescaling by $n^{-1/4}$, to the Brownian sphere.This talk is based on work with Nicolas Curien and with Thomas Meeusen and Bart Zonneveld.