Retrieving the shape in an inverse elasto-acoustic scattering problem: a mathematical investigation and a multi-step solution methodology
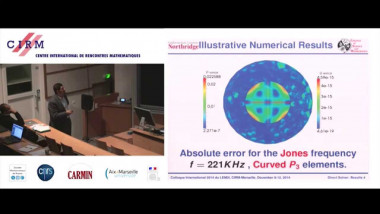
The determination of the shape of an obstacle from its effects on known acoustic waves is an important problem in many technologies such as sonar, geophysical exploration and medical imaging. This inverse obstacle problem (IOP) is difficult to solve, especially from a numerical viewpoint, because of its ill-posed and nonlinear nature. Its investigation requires the understanding of the theory for the associated direct scattering problem, and the mastery of the corresponding numerical solution methods. The main goal of this work is the development of an efficient procedure for retrieving the shape of an elastic obstacle from the knowledge of some scattered far-field patterns, and assuming certain characteristics of the surface of the obstacle. We propose a solution methodology based on a regularized Newton-type method. The solution of the considered IOP by the proposed iterative method incurs, at each iteration, the solution of a linear system whose entries are the Fréchet derivatives of the elasto-acoustic field with respect to the shape parameters. We prove that these derivatives are solutions of the same direct elasto-acoustic scattering problem that differs only in the transmission conditions on the surface of the scatterer. Furthermore, the computational efficiency of the IOP solver depends mainly on the computational efficiency of the solution of the forward problems that arise at each Newton iteration. We propose to solve the direct scattering-type problems using a finite-element method based on discontinuous Galerkin approximations equipped with curved element boundaries. Numerical results will be presented to illustrate the salient features of this computational methodology and highlight its performance characteristics.
acoustics - shape derivative - inverse obstacle problem - Fréchet derivatives - inverse elasto-acoustic scattering problems















![[1247] Dérivation de l'équation de Boltzmann en temps long à partir d'une dynamique de sphères dures](/media/cache/video_light/uploads/video/SeminaireBourbaki.png)
